If you’ve studied your basic Data Structures and Algorithms, then I’m sure you’re familiar with the Queue and the Stack data structures.
In Java, there are a few different ways to implement either of these data structures. But what way is the best way to implement them?
What is the best way to implement a Queue in Java?
What is the best way to implement a Stack in Java?
The Deque Interface
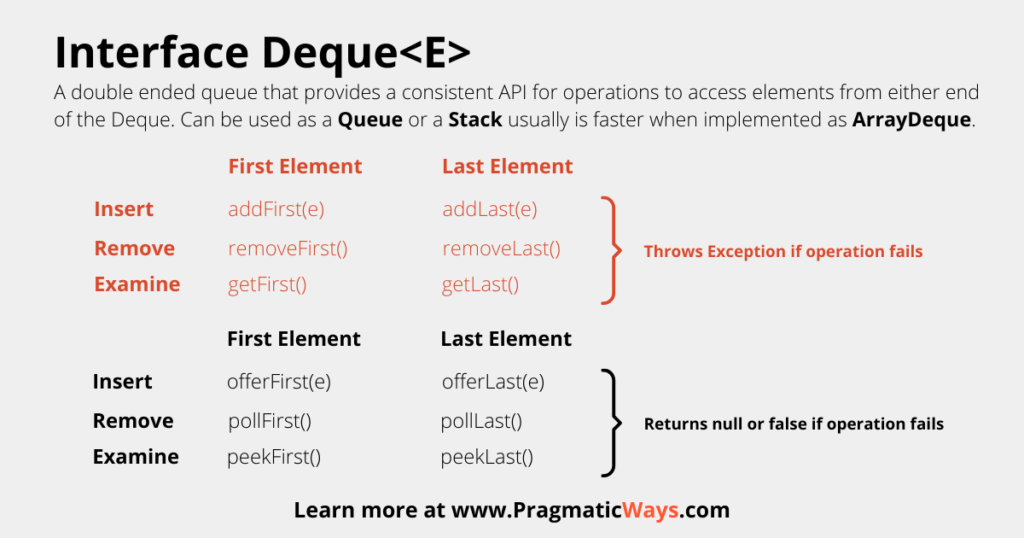
The Deque is a “double ended queue.” As such, it can be used as either a Queue or a Stack. It provides a consistent API for normal operations to add, remove, or peek at elements from either end of the data structure.
The ArrayDeque class implements the Deque interface
Many times, you will want to use the Deque interface as an ArrayDeque. In fact, the Java API documentation even states that the ArrayDeque class will often times be faster than a Queue or a Stack.
This class is likely to be faster than
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/15/docs/api/java.base/java/util/ArrayDeque.htmlStackwhen used as a stack, and faster thanLinkedListwhen used as a queue.
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();Code language: Java (java)Methods for using a Deque as a Queue
Recall that a Queue is a FIFO data structure, or a First In First Out data structure. As such, the Deque interface provides very easy methods for accessing elements at the beginning of the deque.
Methods that throw an exception when the operation fails
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
deque.addFirst(1);
deque.getFirst(); // returns 1 but leaves element in deque
deque.removeFirst(); // returns 1 and removes element from dequeCode language: Java (java)If any of the above methods fail, the Deque interface will throw an exception. This is similar to the Queue interface from Java.
Methods that return null or false when the operation fails
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
deque.offerFirst(1);
deque.peekFirst(); // returns 1 but leaves element in deque
deque.pollFirst(); // returns 1 and removes element from dequeCode language: Java (java)Methods for using a Deque as a Stack
The Stack data structure is a LIFO structure, or a Last In First Out data structure.
What’s nice about the Deque interface is that it doesn’t make you memorize a whole new set of operations for accessing elements from the end of the deque, the methods are identical to modifying from the front as they are from the back.
Methods that throw an exception when the operation fails
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
deque.addLast(1);
deque.getLast(); // returns 1 but leaves element in deque
deque.removeLast(); // returns 1 and removes element from dequeCode language: Java (java)Methods that return null or false when the operation fails
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
deque.offerLast(1);
deque.peekLast(); // returns 1 but leaves element in deque
deque.pollLast(); // returns 1 and removes element from dequeCode language: Java (java)